
Civil engineering is one of the oldest branches of engineering. It incorporates the design and construction of roads, airports, tunnels, bridges, water supply and sewage systems, dams, harbours, railroad systems, docks, power supply systems, buildings, nuclear power plants etc. Civil Engineering has several specialities. Civil engineers work as construction engineers, transportation engineers, hydraulic and irrigation engineers, geotechnical engineers, environmental engineers, public works engineers.
Watch Video| Course | Eligibility | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Diploma in Civil Engineering | Class 10 | 3 years |
| B.E/B.Tech | Class 10+2(PCM) +Entrance Exam | 4 years |
| M.E/M.Tech | B.E/B.Tech+Entrance Exam | 2 years |
| PhD/Doctorate Course | M.E/M.Tech | 3 years |
J.E.E. or Joint Entrance Exam
GUJCET(Gujarat)
MHCET(Maharashtra)
GATE(Graduate Aptitute Test in Engineering)
A graduate course from a private college will cost between INR eighty thousand to INR two lakh per year excluding lodging and boarding expenses. However, in a reputed government institutions fee ranges from INR five thousand to INR twenty thousand per year.
Technical Training.
Mathematical Skills.
Written Communication Skills.
Oral Communication Skills.
Leadership Skills.
Organization Skills.
Problem Solving Skills
Decision Making.
Career in civil engineering is very lucrative. Following are the various job profiles offered to graduates and post graduates in civil engineering. :
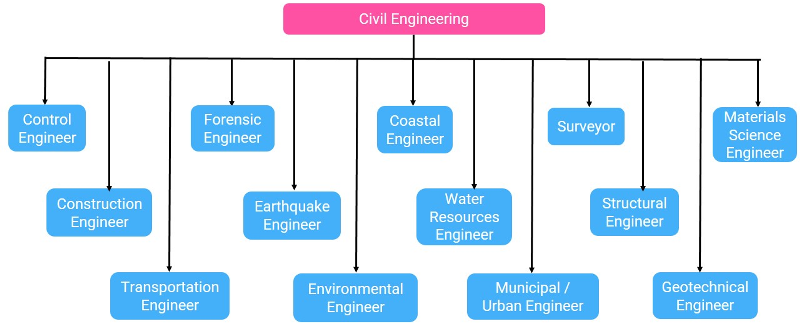
Construction Engineer:They deal with the designing, planning, construction, and management of infrastructures such as highways, bridges, airports, railroads, buildings, dams, and utilities.
Transportation Engineer:They deal with specifying, designing, constructing, and maintaining transportation infrastructure which includes streets, canals, highways, rail systems, airports, ports, and mass transit.
Environmental Engineer:Environmental Engineer deals with treatment of chemical, biological, or thermal wastes, purification of water and air, and remediation of contaminated sites after waste disposal or accidental contamination.
Materials Science Engineer:It studies fundamental characteristics of materials, and deals with ceramics such as concrete and mix asphalt concrete, strong metals such as aluminum and steel, and polymers including polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and carbon fibers. Materials engineering involves protection and prevention (paints and finishes).
Coastal Engineer:Coastal engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerning the specific demands posed by constructing at or near the coast, as well as the development of the coast itself.
Geotechnical Engineer:Geotechnical engineering is important in civil engineering, but also has applications in military, mining, petroleum and other engineering disciplines that are concerned with construction occurring on the surface or within the ground.
Structural Engineer:Structural Engineer utilizes a number of simple structural elements to build complex structural systems. Structural engineers are responsible for making creative and efficient use of funds, structural elements and materials.
Earthquake Engineering:The main objective of earthquake engineering is to foresee the potential consequences of strong earthquakes on urban areas and civil infrastructure. Design, construct and maintain structures to perform at earthquake exposure up to the expectations and in compliance with building codes.
Water Resources Engineering:Water resource engineers analyze and model very small to very large areas of the earth to predict the amount and content of water as it flows into, through, or out of a facility.
Surveyor: A surveyor measures certain dimensions that occur on or near the surface of the earth. Surveyors also lay out the routes of railways, tramway tracks, highways, roads, pipelines and streets as well as position other infrastructure, such as harbors, before construction.
Forensic Engineering:Forensic engineer investigates materials, products, structures or components that fail or do not operate or function as intended, causing personal injury or damage to property.
Municipal or Urban Engineer:Municipal or urban engineering applies the tools of science, art and engineering in an urban environment. Municipal engineering is concerned with municipal infrastructure. This involves specifying, designing, constructing, and maintaining streets, sidewalks, water supply networks, sewers, street lighting, municipal solid waste management and disposal, storage depots for various bulk materials used for maintenance and public works (salt, sand, etc.), public parks and cycling infrastructure.
Control Engineer:Multidisciplinary in nature, control systems engineering activities focus on implementation of control systems mainly derived by mathematical modeling of systems of a diverse range.
Civil and Structural Engineering
Civil Engineering
Structural Engineering
Environment Engineering
Geotechnical Engineering
Construction Managemet
Traffic and Transportation Engineering
Hydraulics and Water Resources Engineering
Geo-Informatics
Transportation Engineering
Water Resource Engineering
IIT Gandhinagar (http://www.iitgn.ac.in )
Sardar Vallabhbhai Institute of Technology, Anand.( http://svitvasad.ac.in)
Parul Institute Of Technology, Vadodara ( https://www.paruluniversity.ac.in)
Sardar Vallabhbhai National Institute of Technology, Surat ( http://www.svnit.ac.in)
Nirma University institute of technology, Ahmedabad ( http://www.nirmauni.ac.in/ITNU/CE/Courses)
Sarvajanik college of Engineering and Technology (https://scet.ac.in )
Sardar Patel College of Engineering, Andheri (West), Mumbai. (http://www.spce.ac.in)
Maharashtra Institute of Technology, Kothrud, Pune. (http://www.mitpune.ac.in)
Government College of Engineering, Aurangabad. (http://geca.ac.in/home.aspx)
Government College of Engineering, Karad. (http://www.gcekarad.ac.in)
Government College of Engineering, Amravat. (https://gcoea.ac.in)
IIT Kharagpur. (http://www.iitkgp.ac.in/academics/?page=acads)
IIT Bombay. (https://www.civil.iitb.ac.in)
IIT Madras. (https://www.iitm.ac.in)
IIT Dehli.(http://civil.iitd.ac.in)
Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani.(http://www.bits-pilani.ac.in)
IIT Guwahati (http://www.iitg.ac.in)
Institute of Technology, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi(http://www.iitbhu.ac.in)
National Institute of Technology, Karnataka.(http://civil.nitk.ac.in)
Afcons Infrastructure Limited.
Punj Lloyd.
Newton Engineering & Chemical Ltd.
Akme Projects Ltd.
L & T Engineering & Contruction Division.
Hindustan Contruction Company.
Note:
All the students, teachers and guardians should note that the above mentioned websites and information on various colleges / universities may change under the rules and regulations of the education department.